Did you know that your gut health plays a crucial role in your overall health and well-being?
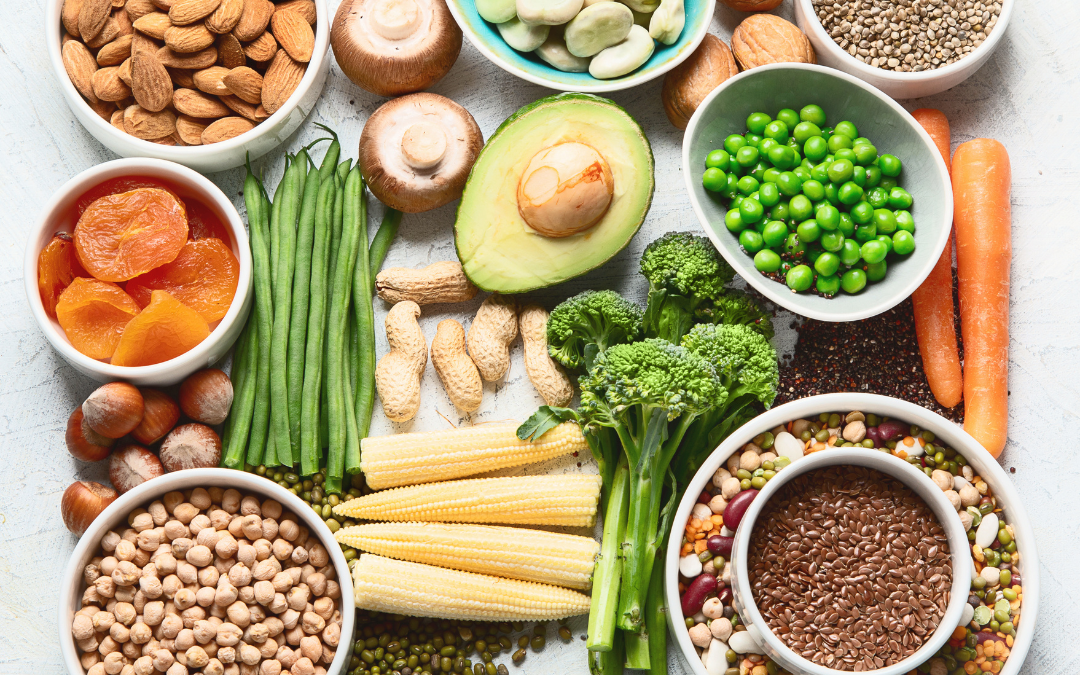
One of the best ways to support a healthy gut is by eating a diverse range of plant foods. By consuming 30 different types of fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes each week, you can promote a healthy gut microbiome and enjoy a range of health benefits. Research shows that a diverse diet can improve digestion, reduce inflammation, and boost your immune system.
Plus, eating a plant-based diet can also help promote environmental sustainability by reducing your reliance on resource-intensive animal products.
In this article, I’ll explore the many benefits of eating 30 different plant foods a week for gut health and provide practical tips for incorporating more plant-based foods into your diet. Whether you’re looking to improve your gut health or just want to enjoy the many benefits of a plant-based diet, this article has everything you need to get started.
Whole Foods, Not Processed

Feeding the Microbiome:
Eating a diverse range of plant foods is one of the best ways to support a healthy gut microbiome. The gut microbiome is a collection of trillions of microorganisms that live in your digestive tract. These microorganisms play a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function.
Research suggests that a diverse diet that includes a wide range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can promote a healthy gut microbiome by increasing the variety and number of beneficial gut bacteria. This, in turn, can help reduce inflammation, improve digestion, and boost immune function.
For example, eating fibre-rich plant foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help feed the beneficial bacteria in your gut, leading to an increase in short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which have been shown to improve gut health by reducing inflammation and promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
In addition, research has shown that a diverse diet can also help reduce the risk of gut-related diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and colorectal cancer. A review published in the National Library of Medicine found that a diet diverse in fibre, fruits and vegetables was associated with a reduced risk of IBD.
Overall, incorporating 30 different types of plant foods into your diet each week can have a powerful impact on your gut health, promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, reducing inflammation, and reducing the risk of gut-related diseases.
Further Health and Environmental Benefits:
Nutrient diversity:
Eating a variety of plant foods ensures that you consume a range of vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients that are important for overall health and well-being. Some plant foods are high in certain nutrients, while others are high in different ones, so consuming a diverse range of plant foods can help ensure that you get everything your body needs.
Disease prevention:
Eating a variety of plant foods has been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. The abundance of antioxidants and phytochemicals found in plant foods can help protect against cellular damage and inflammation, which can contribute to the development of chronic diseases.
Environmental sustainability:
Eating a diverse range of plant foods can also have positive environmental implications. By consuming a variety of plant-based foods, you can reduce your reliance on resource-intensive animal products and promote more sustainable food systems. This can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, conserve water, and protect natural habitats.
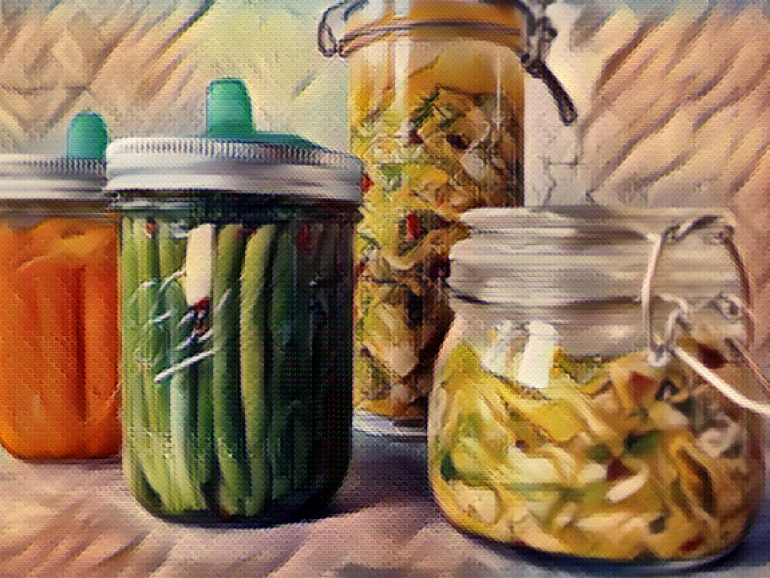
The Power of Fermented Foods:
Fermented foods are beneficial to the microbiome because they are rich in probiotics, which are live bacteria and yeasts that are good for your health, especially your gut health. When consumed, probiotics help increase the number and diversity of beneficial bacteria in the gut microbiome, leading to a healthier gut environment.
Many fermented foods are created through lacto-fermentation, which involves dry-salting vegetables and fermenting them in their own juices or soaking vegetables or grains in a salty brine for some time. During this process, naturally occurring bacteria consume the sugars and starches in the food, creating lactic acid, which acts as a natural preservative and gives the food its tangy flavour.
Some examples of fermented foods include sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, tempeh, kefir, and yoghurt. These foods contain a variety of beneficial bacteria strains, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which can help improve gut health by increasing the number of beneficial bacteria in the gut, promoting healthy digestion, and reducing inflammation.
Research has also linked the consumption of fermented foods to a range of health benefits, including improved immune function, lower cholesterol levels, and a reduced risk of certain diseases such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Overall, adding fermented foods to your diet is a simple and delicious way to support your gut health. They promote a healthy microbiome and help you get closer to that 30 plant foods target.

Tips for Adding 30 Different Plant Foods to Your Diet Each Week:
Start with small changes:
Incorporating more plant foods into your diet doesn’t have to be an all-or-nothing endeavour. Start by making small changes, like adding a serving of vegetables to your lunch or swapping out a meat-based meal for a plant-based one once a week.
Stock up on staples:
Keeping a well-stocked pantry and fridge can make it easier to incorporate more plant foods into your diet. Some staples to consider include whole grains like quinoa and brown rice, beans and legumes, nuts and seeds, and a variety of fruits and vegetables.
Embrace herbs and spices:
Herbs and spices are not only a delicious way to add flavour and depth to your meals. They provide a range of health benefits and count towards your 30 plant foods. Many herbs and spices are rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, which can help reduce inflammation in the body and protect against chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Try new recipes:
Experimenting with new recipes can be a fun way to incorporate more plant-based foods into your diet. Look for recipes that feature fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes as the main ingredients, and try to incorporate different herbs and spices to add flavour.
Have you tried this Eastern-Spiced Stuffed Squash Recipe I recently shared on Social Media? This dish contains several varieties of plant foods.
What about this chickpea shakshouka with cauliflower rice?
Explore different cuisines:
Different cuisines often rely heavily on plant-based foods, so exploring different types of cuisine can be a great way to incorporate more plant-based foods into your diet. Consider trying dishes from cultures that emphasize plant-based eating, such as Indian, Middle Eastern, and Mediterranean cuisines.
Make swaps:
Swapping out animal products for plant-based alternatives can be an easy way to incorporate more plant-based foods into your diet. For example, try swapping out meat for tofu or tempeh in stir-fries, or using cashew cream instead of dairy cream in soups and sauces.
Avoid Super Processed Foods (SPFs)
Plant Foods: Embrace the Power of 30 Now!
Eating 30 different plant foods a week can have a powerful impact on your gut health and overall well-being.
By consuming a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, you can promote a healthy gut microbiome, reduce inflammation, and reduce the risk of gut-related diseases.
In addition, incorporating fermented foods into your diet can also provide a wealth of health benefits by increasing the number and diversity of beneficial bacteria in your gut.
By following these practical tips for incorporating more plant-based foods into your diet, you can enjoy the many benefits of a diverse and plant-rich diet, from better gut health to improved immune function and beyond.
Are You Ready to Change Your Gut Story?
You don’t have to manage this alone. Take the first step to feeling better today.

